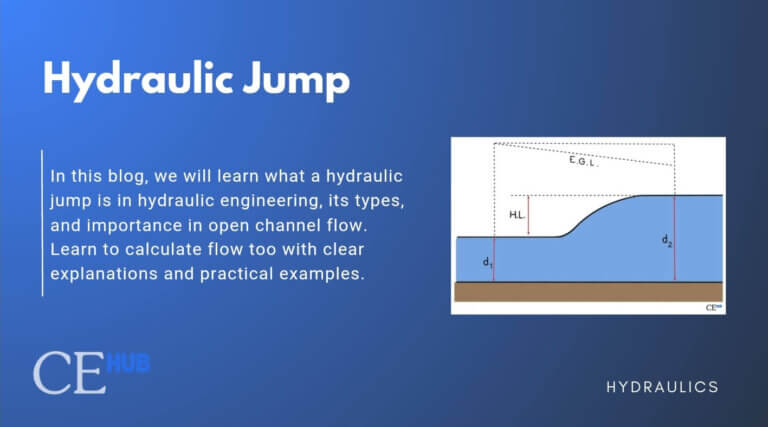
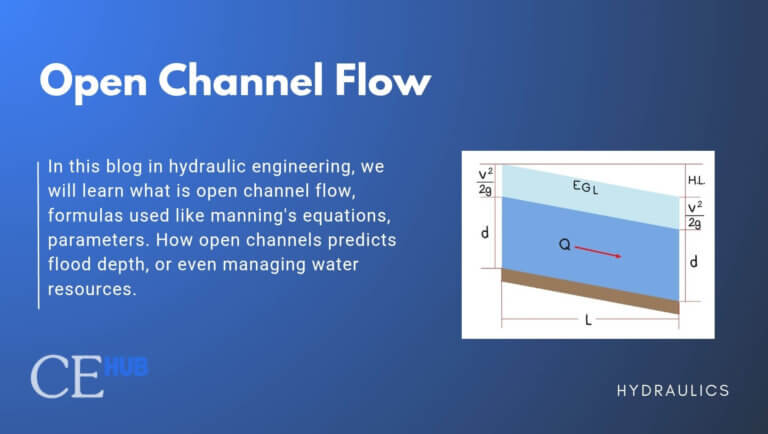
Basic Fluid Properties
What you’ll learn
Fluids, which include both liquids and gases, are fundamental in fluid mechanics, where their behavior is analyzed based on key properties that influence motion, pressure, and flow dynamics. These properties determine how fluids respond to external forces and interact with their surroundings in various engineering applications.
Density
Density is the ratio of mass of fluid and its volume. It represents how much matter is packed into a given space and is one of the most fundamental fluid properties.
![]()
Where:![]() =density
=density![]() =mass
=mass![]() =volume
=volume
Typical Values
| Fluid | Density ( |
| Water | 998 |
| Air | 1.2 |
| Mercury | 13560 |
| Glycerin | 1260 |
Example
The glycerin has a mass of 1200 kg and a volume of 0.952 cu.m. Find its density?
![]()
![]()
![]()
Specific Volume
Specific volume occupied by a unit mass of fluid. It is the reciprocal of density and is particularly useful in thermodynamic analysis.
![]()
where:![]() =specific volume
=specific volume![]()
V=volume![]()
m=mass(kg)![]() =density
=density![]()
Specific Weight
Specific weight (also called unit weight) is the weight of fluid per unit volume. It represents the gravitational force exerted by a fluid per unit volume.
Where:![]() = specific weight
= specific weight
W = weight (N)
V = volume ![]()
![]() = density
= density ![]()
g = gravity acceleration
Example
Specific Gravity of an oil is 0.82. Determine its specific weight
Specific Gravity
Specific gravity (relative density) is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance.
![]()
where:![]() =density of the fluid
=density of the fluid![]() =density of the water
=density of the water![]() =specific weight of the fluid
=specific weight of the fluid ![]() =specific weight of the water
=specific weight of the water
Bulk Modulus of Elasticity
Bulk modulus of elasticity measures a fluid’s resistance to compression. It quantifies how much pressure is required to produce a given fractional change in volume.
Example
A liquid compressed in a cylinder has a volume of 1000 cu.m at ![]() and a volume of
and a volume of ![]() at
at ![]() . What is its bulk modulus of elasticity?
. What is its bulk modulus of elasticity?
Compressibility
Compressibility is the reciprocal of the bulk modulus. It measures how much a material decreases in volume when subjected to pressure.
![]()
Types of Compressibility
Isothermal Compressibility
Volume change at constant temperature
Adiabatic Compressibility
Volumes changed without heat transfer
Example
If the Bulk Modulus of Water is 2.2 GPa. What is its coefficient of Compressibility?
Viscosity
Viscosity is defined as the fluid’s resistance to flow. It represents internal friction between fluid layers moving at different velocities.
Types of Viscosity
Dynamic Viscosity
Units: poise or 0.1 Pa-s
where:![]() =shear stress (Pa)
=shear stress (Pa)![]() =dynamic viscosity
=dynamic viscosity ![]()
![]() =velocity gradient (
=velocity gradient (![]() )
)
Kinematic Velocity
![]()
where:![]() =kinematic viscosity
=kinematic viscosity ![]() =dynamic viscosity
=dynamic viscosity ![]() =density
=density
Surface Tension
The force responsible for the tension that acts along its surface and arises from the attractive forces between the liquid’s molecules. The strength of this force per unit length is known as surface tension.
Capillary Action
is when liquid rise or fall through narrow spaces without external forces.
References
J. D. Anderson Modern Compressible Flow with Historical Perspective, 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003.
F L U I D M E C H A N I C S FUNDAMENTALS AND APPLICATIONS Third Edition. (n.d.). https://engineeringbookslibrary.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/fluid-mechanics-fundamentals-and-applications-3rd-edition-cengel-and-cimbala-2014.pdf